seaborn.color_palette#
- seaborn.color_palette(palette=None, n_colors=None, desat=None, as_cmap=False)#
Return a list of colors or continuous colormap defining a palette.
- Possible
palettevalues include: Name of a seaborn palette (deep, muted, bright, pastel, dark, colorblind)
Name of matplotlib colormap
‘husl’ or ‘hls’
‘ch:<cubehelix arguments>’
‘light:<color>’, ‘dark:<color>’, ‘blend:<color>,<color>’,
A sequence of colors in any format matplotlib accepts
Calling this function with
palette=Nonewill return the current matplotlib color cycle.This function can also be used in a
withstatement to temporarily set the color cycle for a plot or set of plots.See the tutorial for more information.
- Parameters:
- paletteNone, string, or sequence, optional
Name of palette or None to return current palette. If a sequence, input colors are used but possibly cycled and desaturated.
- n_colorsint, optional
Number of colors in the palette. If
None, the default will depend on howpaletteis specified. Named palettes default to 6 colors, but grabbing the current palette or passing in a list of colors will not change the number of colors unless this is specified. Asking for more colors than exist in the palette will cause it to cycle. Ignored whenas_cmapis True.- desatfloat, optional
Proportion to desaturate each color by.
- as_cmapbool
If True, return a
matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap.
- Returns:
- list of RGB tuples or
matplotlib.colors.ListedColormap
- list of RGB tuples or
See also
set_paletteSet the default color cycle for all plots.
set_color_codesReassign color codes like
"b","g", etc. to colors from one of the seaborn palettes.
Examples
Calling with no arguments returns all colors from the current default color cycle:
sns.color_palette()
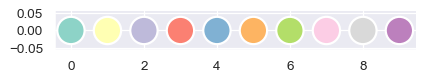
Other variants on the seaborn categorical color palette can be referenced by name:
sns.color_palette("pastel")
Return a specified number of evenly spaced hues in the “HUSL” system:
sns.color_palette("husl", 9)
Return all unique colors in a categorical Color Brewer palette:
sns.color_palette("Set2")
Return a diverging Color Brewer palette as a continuous colormap:
sns.color_palette("Spectral", as_cmap=True)
Return one of the perceptually-uniform palettes included in seaborn as a discrete palette:
sns.color_palette("flare")
Return one of the perceptually-uniform palettes included in seaborn as a continuous colormap:
sns.color_palette("flare", as_cmap=True)
Return a customized cubehelix color palette:
sns.color_palette("ch:s=.25,rot=-.25", as_cmap=True)
Return a light sequential gradient:
sns.color_palette("light:#5A9", as_cmap=True)
Return a reversed dark sequential gradient:
sns.color_palette("dark:#5A9_r", as_cmap=True)
Return a blend gradient between two endpoints:
sns.color_palette("blend:#7AB,#EDA", as_cmap=True)
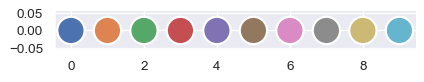
Use as a context manager to change the default qualitative color palette:
with sns.color_palette("Set3"): sns.relplot(x=x, y=y, hue=hue, s=500, legend=False, height=1.3, aspect=4) sns.relplot(x=x, y=y, hue=hue, s=500, legend=False, height=1.3, aspect=4)
See the underlying color values as hex codes:
print(sns.color_palette("pastel6").as_hex())
['#a1c9f4', '#8de5a1', '#ff9f9b', '#d0bbff', '#fffea3', '#b9f2f0']
- Possible