seaborn.clustermap#
- seaborn.clustermap(data, *, pivot_kws=None, method='average', metric='euclidean', z_score=None, standard_scale=None, figsize=(10, 10), cbar_kws=None, row_cluster=True, col_cluster=True, row_linkage=None, col_linkage=None, row_colors=None, col_colors=None, mask=None, dendrogram_ratio=0.2, colors_ratio=0.03, cbar_pos=(0.02, 0.8, 0.05, 0.18), tree_kws=None, **kwargs)#
Plot a matrix dataset as a hierarchically-clustered heatmap.
This function requires scipy to be available.
- Parameters:
- data2D array-like
Rectangular data for clustering. Cannot contain NAs.
- pivot_kwsdict, optional
If
datais a tidy dataframe, can provide keyword arguments for pivot to create a rectangular dataframe.- methodstr, optional
Linkage method to use for calculating clusters. See
scipy.cluster.hierarchy.linkage()documentation for more information.- metricstr, optional
Distance metric to use for the data. See
scipy.spatial.distance.pdist()documentation for more options. To use different metrics (or methods) for rows and columns, you may construct each linkage matrix yourself and provide them as{row,col}_linkage.- z_scoreint or None, optional
Either 0 (rows) or 1 (columns). Whether or not to calculate z-scores for the rows or the columns. Z scores are: z = (x - mean)/std, so values in each row (column) will get the mean of the row (column) subtracted, then divided by the standard deviation of the row (column). This ensures that each row (column) has mean of 0 and variance of 1.
- standard_scaleint or None, optional
Either 0 (rows) or 1 (columns). Whether or not to standardize that dimension, meaning for each row or column, subtract the minimum and divide each by its maximum.
- figsizetuple of (width, height), optional
Overall size of the figure.
- cbar_kwsdict, optional
Keyword arguments to pass to
cbar_kwsinheatmap(), e.g. to add a label to the colorbar.- {row,col}_clusterbool, optional
If
True, cluster the {rows, columns}.- {row,col}_linkage
numpy.ndarray, optional Precomputed linkage matrix for the rows or columns. See
scipy.cluster.hierarchy.linkage()for specific formats.- {row,col}_colorslist-like or pandas DataFrame/Series, optional
List of colors to label for either the rows or columns. Useful to evaluate whether samples within a group are clustered together. Can use nested lists or DataFrame for multiple color levels of labeling. If given as a
pandas.DataFrameorpandas.Series, labels for the colors are extracted from the DataFrames column names or from the name of the Series. DataFrame/Series colors are also matched to the data by their index, ensuring colors are drawn in the correct order.- maskbool array or DataFrame, optional
If passed, data will not be shown in cells where
maskis True. Cells with missing values are automatically masked. Only used for visualizing, not for calculating.- {dendrogram,colors}_ratiofloat, or pair of floats, optional
Proportion of the figure size devoted to the two marginal elements. If a pair is given, they correspond to (row, col) ratios.
- cbar_postuple of (left, bottom, width, height), optional
Position of the colorbar axes in the figure. Setting to
Nonewill disable the colorbar.- tree_kwsdict, optional
Parameters for the
matplotlib.collections.LineCollectionthat is used to plot the lines of the dendrogram tree.- kwargsother keyword arguments
All other keyword arguments are passed to
heatmap().
- Returns:
ClusterGridA
ClusterGridinstance.
See also
heatmapPlot rectangular data as a color-encoded matrix.
Notes
The returned object has a
savefigmethod that should be used if you want to save the figure object without clipping the dendrograms.To access the reordered row indices, use:
clustergrid.dendrogram_row.reordered_indColumn indices, use:
clustergrid.dendrogram_col.reordered_indExamples
Plot a heatmap with row and column clustering:
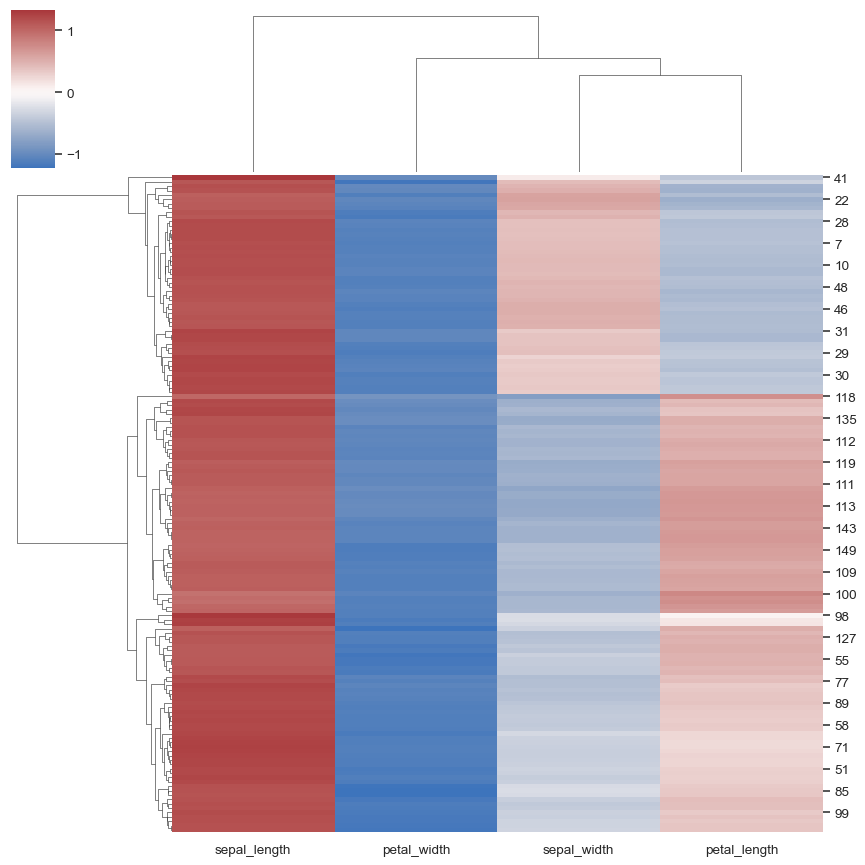
iris = sns.load_dataset("iris") species = iris.pop("species") sns.clustermap(iris)
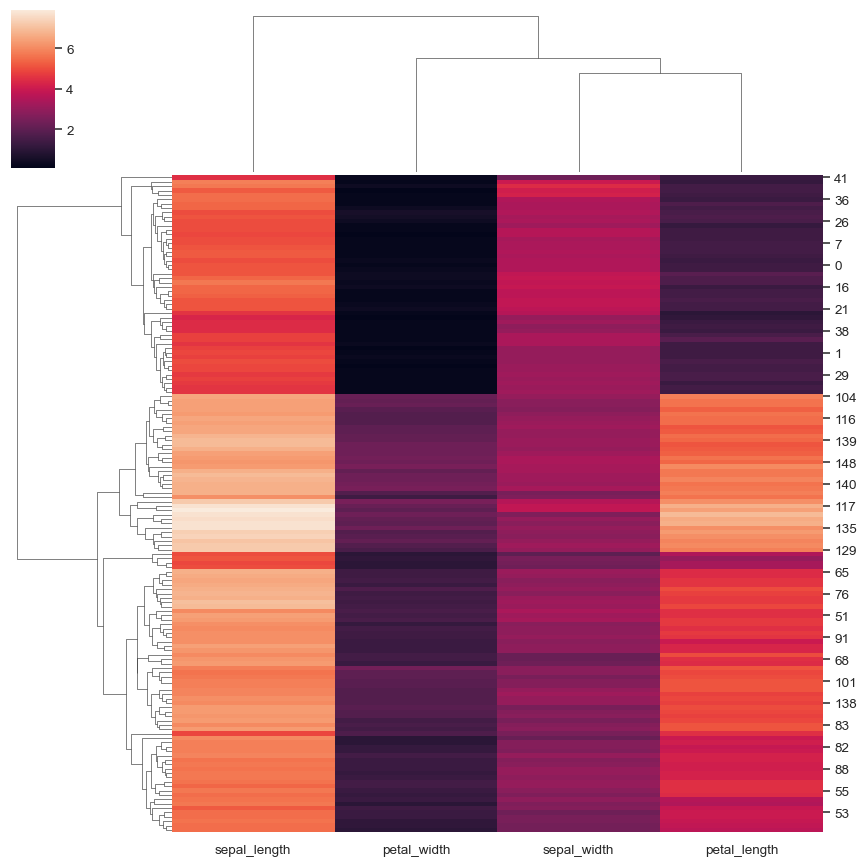
Change the size and layout of the figure:
sns.clustermap( iris, figsize=(7, 5), row_cluster=False, dendrogram_ratio=(.1, .2), cbar_pos=(0, .2, .03, .4) )
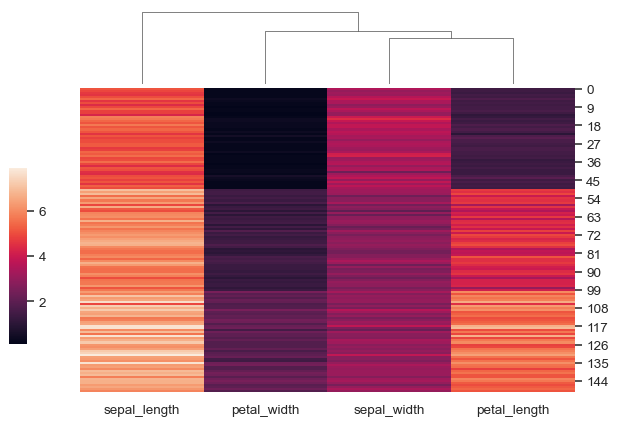
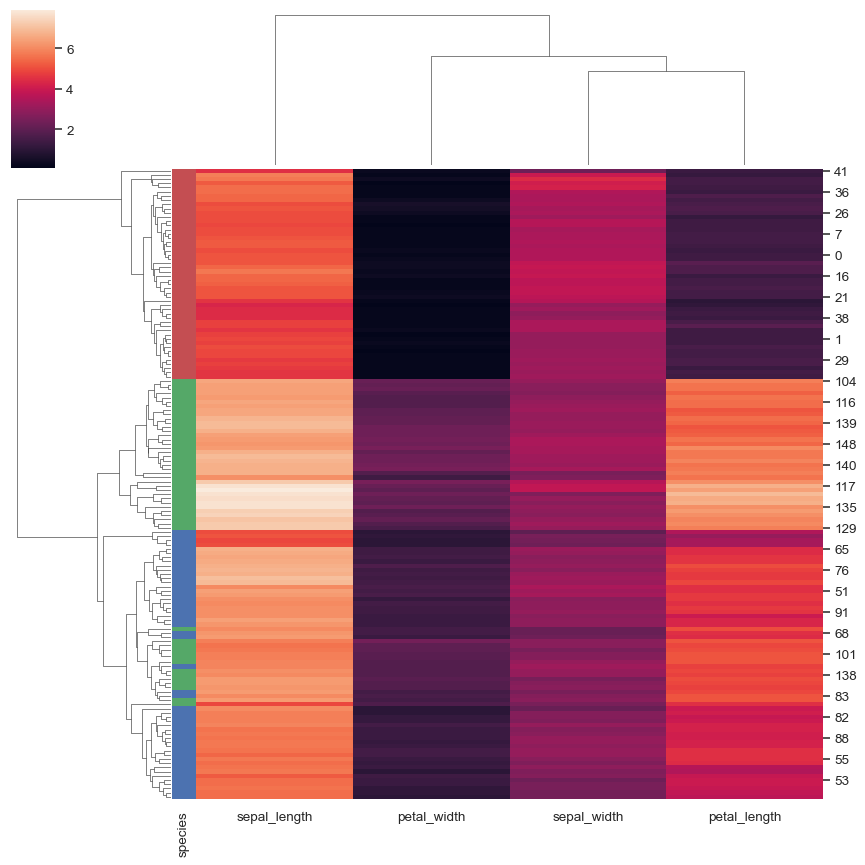
Add colored labels to identify observations:
lut = dict(zip(species.unique(), "rbg")) row_colors = species.map(lut) sns.clustermap(iris, row_colors=row_colors)
Use a different colormap and adjust the limits of the color range:
sns.clustermap(iris, cmap="mako", vmin=0, vmax=10)
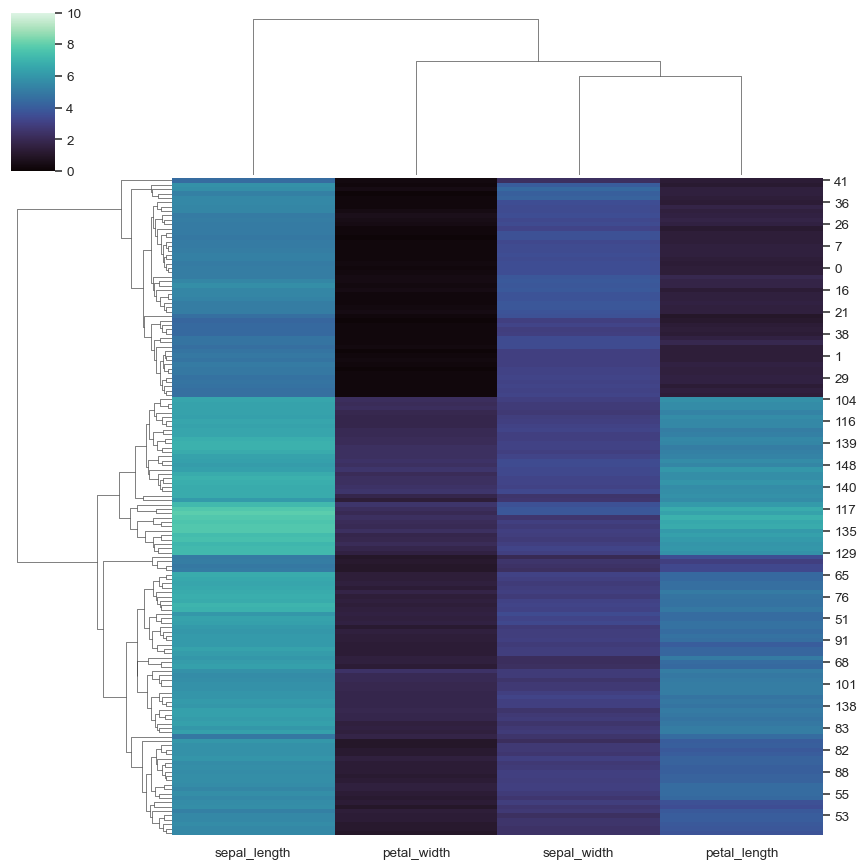
Use differente clustering parameters:
sns.clustermap(iris, metric="correlation", method="single")
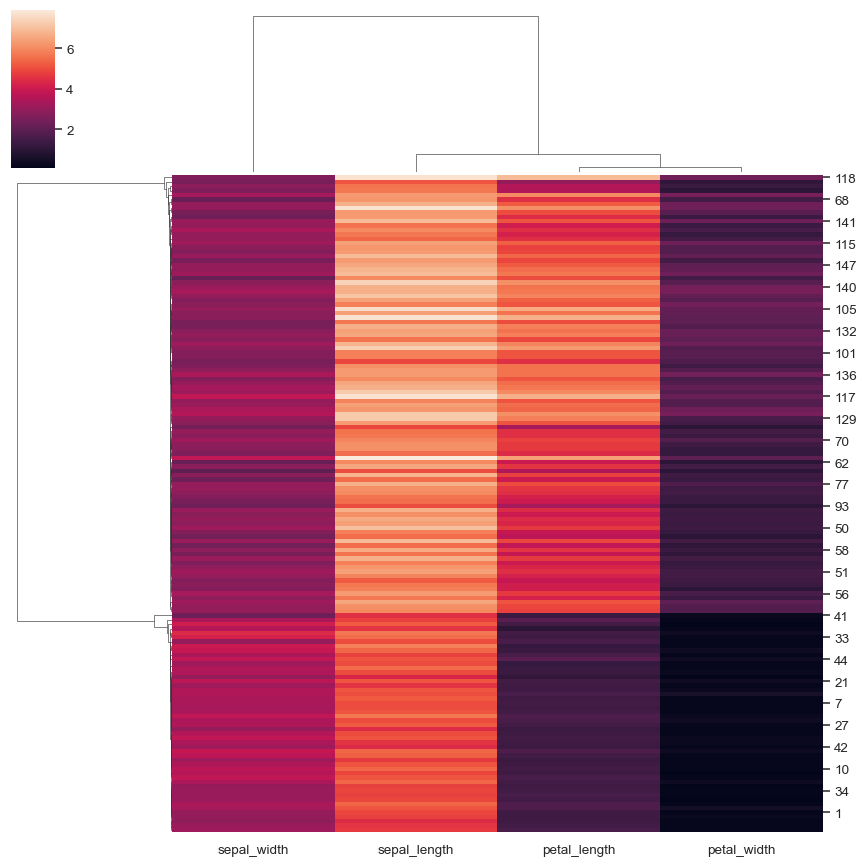
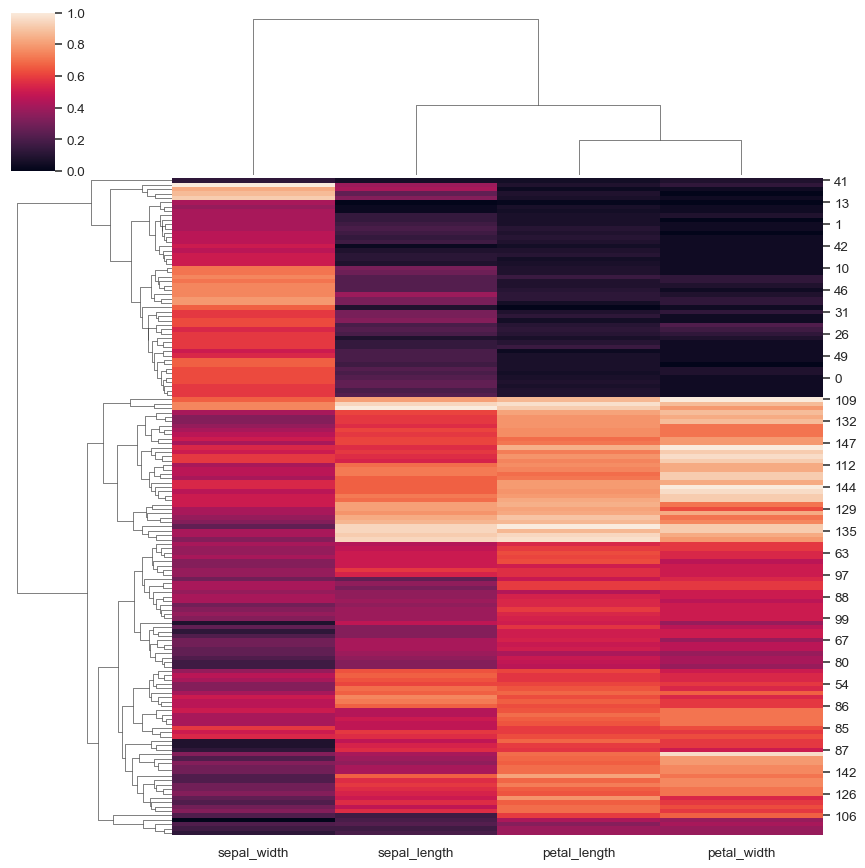
Standardize the data within the columns:
sns.clustermap(iris, standard_scale=1)
Normalize the data within rows:
sns.clustermap(iris, z_score=0, cmap="vlag", center=0)